The continuing cryptocurrency bear market has triggered an enormous loss of Bitcoin (BTC) mining profitability as BTC mining expenses outpace the cost of Bitcoin.
Carefully associated with the stop by the BTC cost, Bitcoin mining profitability continues to be tanking since late 2021 and arrived at its cheapest multi-month levels at the begining of This summer 2022.
Based on data from crypto tracking website Bitinfocharts, BTC mining profitability tumbled to as little as $.07 each day per 1 terahash per second (THash/s) on This summer 1, 2022, touching the cheapest level since October 2020.
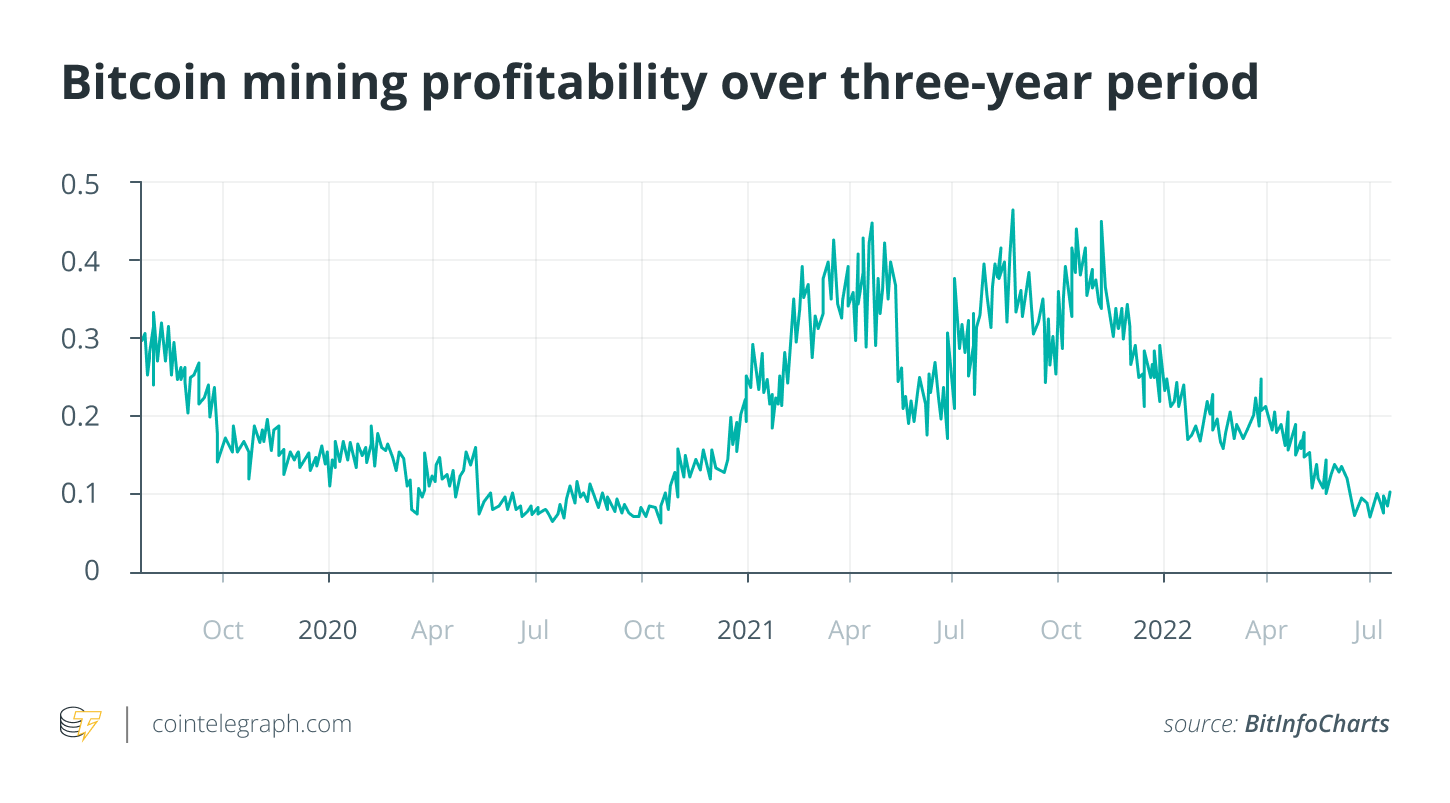
The loss of BTC mining profitability is responsible for some big alterations in the crypto mining industry.
Lower Bitcoin prices fueled selling pressure as miners were pressed to market their BTC to carry on mining and purchase electricity. Nearly all big crypto mining firms like Core Scientific needed to sell a lot of Bitcoin to live the challenging market conditions.
The growing unprofitability of BTC mining has additionally triggered a large stop by interest in crypto mining devices, causing many miners to sell their mining hardware for a cheap price.
As affordable prices of application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) miners and graphics processing units (GPU) may drive more interest from new miners, it’s crucial to understand that the cost of mining hardware is simply one from many reasons for BTC mining profitability.
What’s Bitcoin mining profitability and just how could it be defined?
Bitcoin mining is definitely an business activities which involves producing digital currency Bitcoin while using computing power GPU-based miners or particularly-designed ASIC miners.
Bitcoin mining profitability is really a measure defining the amount that a Bitcoin miner yields profit with different wide quantity of factors, such as the cost of Bitcoin, the mining difficulty, the price of energy, the kind of mining hardware yet others.
Factor 1: Bitcoin cost and block rewards
The cost of Bitcoin is among the most apparent factors impacting the BTC mining profitability as the need for BTC is directly proportional to profits produced by miners.
Bear markets trigger even more focus on BTC cost from miners simply because they risk taking a loss if BTC drops below a particular cost level.
Miners should take into consideration the quantity of the block reward or the quantity of BTC provided to miners for mining one block around the BTC blockchain. Bitcoin’s original block reward amounted up to 50 BTC prior to being cut to the present 6.5 BTC following three historic block reward halvings.
Bitcoin halvings really are a main issue with the BTC protocol, planning to decrease the amount of the brand new coins entering the network by cutting the block reward in two every 210,000 blocks or roughly every 4 years.
Factor 2: Bitcoin mining hardware characteristics
Bitcoin mining profitability largely depends upon the option of a BTC mining tool and related characteristics including hash rate, power consumption and cost.
Hash rates are the processing power a miner, measured in hashes per second (H/S). Greater hash rates include representations in kilohashes per second (KH/S), gigahashes per second (GH/S), terahashes per second (TH/S), exahashes per second (EH/S) and so forth.
A miner’s hash rates are the rate where it may solve crypto mining puzzles to mine Bitcoin. The faster the rate, the greater BTC is found inside a specific time-frame. Because the BTC hash rates are constantly breaking new highs, Bitcoin miner manufacturers regularly produce new mining devices supporting greater hash rates, while older miners apparently become obsolete with time.
Another essential feature of the BTC mining system is the power consumption. With rising global energy costs, a miner’s capability to consume less energy is important.
The cost of actual mining devices can also be an essential expense when calculating the BTC mining profitability. Both GPU and ASIC miners got cheaper among the bear market this season, but completely new flagship miners still are more expensive than $11,000 during the time of writing.
Factor 3: Mining difficulty and hash rate
Bitcoin mining difficulty is really a way of measuring how hard it’s to mine a BTC block, having a greater difficulty requiring additional computing capacity to verify transactions and mine new coins.
Network difficulty continues to be rising in 2022, constantly breaking new all-time highs. Bitcoin’s mining difficulty adjustment occurs every 2,016 blocks, or about every two days, as Bitcoin is developed to self-adjust to be able to conserve a target block duration of ten minutes.
The Bitcoin hash rates are another fundamental metric for assessing the effectiveness of the BTC network, like a greater hashrate means more computing power is needed to ensure and add transactions towards the blockchain. This makes BTC safer since it would take more miners in addition to more time and energy to consider within the network.
Factor 4: Discovered another means
The cost of electricity is yet another essential aspect when calculating the profitability of BTC mining.
Miners consider electricity prices in a variety of countries in compliance with local crypto mining rules. As mining activity puts extra force on an electrical grid, it’s vital that you double-check local needs and particular energy prices for powering BTC miners in a country or region.
Bitcoin mining could be operated by many powers, both renewable like solar and wind power and nonrenewable sources including non-renewable fuels like coal, oil and gas. Among soaring energy prices brought on by recent supply issues, miners should pay special focus on possible implications on BTC mining earnings when utilizing nonrenewable energy.
Factor 5: Pool fee otherwise mining solo
Many Bitcoin miners choose to join mining pools rather of being employed as individual miners. That’s a method to combine their computing power while increasing the likelihood of locating a block and mining BTC faster.
Pool miners should know another small expense that’s taken by pool admins that setup the program for this kind of mining. The charge is usually 1-3% from the miner’s individual reward, with respect to the pool.
Factor 6: Other outlays
Bitcoin mining expenses aren’t only at ASICs and GPUs and network indicators. BTC mining might also require extra investment associated with the physical mining setup, including facilities and property that make the perfect fit. Significant expenses can include cooling or noise canceling equipment as some miner machines are connected having a lots of of warmth and environmental noise.
Crypto mining calculators
Among the simplest ways to calculate Bitcoin mining profitability according to all of the listed factors is applying online BTC mining calculators.
Made to simplify the entire process of calculating Bitcoin mining profitability, a BTC mining calculator predicts the approximate mining earnings according to inputs like BTC cost, hash rate, electricity cost yet others.
Let’s take a good example of calculating Bitcoin mining profitability having a completely new Bitmain ASIC Antminer S19 Pro while using BTC mining calculator by crypto market data provider CryptoCompare.
Antminer S19 Pro includes a maximum hashrate of 110TH/s and power use of 3250W. Let’s think that a miner’s pool fee is 2% and also the miner relies in North Dakota, in which the average residential electricity rate in 2022 amounts to roughly $.11, in comparison to the U . s . States national average cost of roughly $.14.
Related: BTC mining costs achieve 10-month lows as miners use more effective rigs
Given these variables, the daily profit ratio makes up about 27%, with possible BTC mining profits amounting to $70 monthly, or $840 each year, based on CryptoCompare. In comparison, because of the U.S. national average electricity cost of $.14, the daily profit ratio amounts to % or perhaps generates a loss of revenue using the current BTC cost along with other network indicators.


