For the good that Bitcoin has, additionally, it offers a generally recognized issue in scalability. Bitcoin are only able to process a restricted quantity of transactions per block and, by August. 17, 2022, are designed for about five transactions per second, which compared to other blockchains is low. The factor restricting scalability is based on Bitcoin’s cryptographic formula.
The Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Formula (ECDSA) may be the essential cryptographic formula that forces Bitcoin and helps to ensure that just the rightful owner have access to and manage their. Presently, verification from the ECDSA, a Bitcoin signature allowing to handle transactions and send Bitcoin (BTC), isn’t efficient and limits the scalability from the Bitcoin blockchain. A possible option would be using zero-understanding proof (ZKP) technology, allowing greater levels of security and privacy.
A current Starkware paper is definitely the way of efficiently verifying ECDSA from inside the STARK ecosystem, potentially resolving the blockchain trilemma for Bitcoin — i.e., achieving scalability, security and decentralization concurrently.
Foundations from the technology
A ZKP is really a cryptographic technique that allows the prover to verify someone else’s claim without supporting data. ZKPs are cryptographic protocols that keep organizations from users’ privacy. ZKPs is yet another useful foundation for a lot of cryptographic protocols, making certain participants stick to the protocol’s specifications. Privacy and scalability are enhanced with ZKPs since certain information is revealed and transacted without disclosing all the details that should be proven.
In line with the ZKP technology, STARKs, or Scalable Transparent Argument of Understanding — introduced by Starkware — is a kind of cryptographic proof technology that assists you to communicate data with a 3rd party — e.g., sign transactions without revealing the information. Additionally, it enables moving computations and storage of validated data off-chain, thus growing scalability.
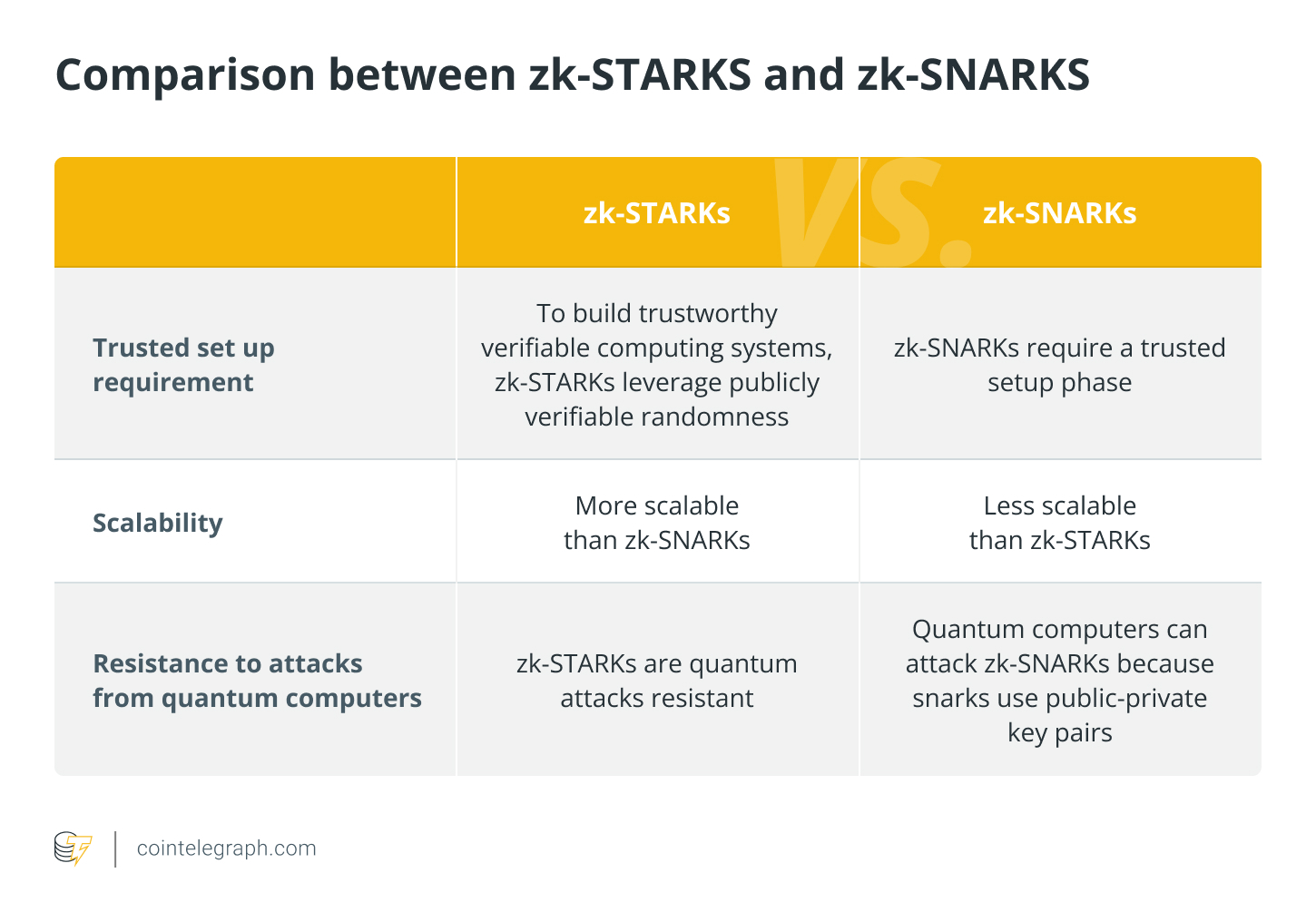
STARKs is really a quantum-resistant system according to hash functions utilized by Ethereum, not elliptic curves employed by Bitcoin. Importantly, STARKs systems are thought greater than the earlier versions, zk-SNARKs, and may resist attacks from quantum computers.
EC-STARKs: The next phase in Bitcoin’s scalability?
Earlier, Starkware announced governance token issuance because of its StarkNet — a decentralized permissionless STARK-based validity rollup that operates being an Ethereum layer-2 chain — to decentralize the network further and keep STARK technology like a public good. However, Ethereum’s underlying storage cost constraints the scalability the best-selling technology. However, its application for that Bitcoin blockchain may present a much better platform for decentralized applications soon.
Related: zk-STARKs versus. zk-SNARKs described
EC-STARKs are generation x of the technology, planning to increase Bitcoin’s scalability and security by replacing hash functions with elliptic curves — i.e., making already-existing scalability solutions for Ethereum to become suitable for Bitcoin. With EC-STARKs, it’s possible to run an off-chain protocol for Bitcoin and proofs in STARK. To put it simply, Bitcoin could be emulated inside STARK, allowing highly sophisticated protocols to become built on Bitcoin-backed tokens with similar elliptic curve keys.
Thus, utilizing fraxel treatments might not only boost the scalability of Bitcoin but function as the gateway for developers to produce DApps on Bitcoin, potentially developing a rival for Ethereum.


