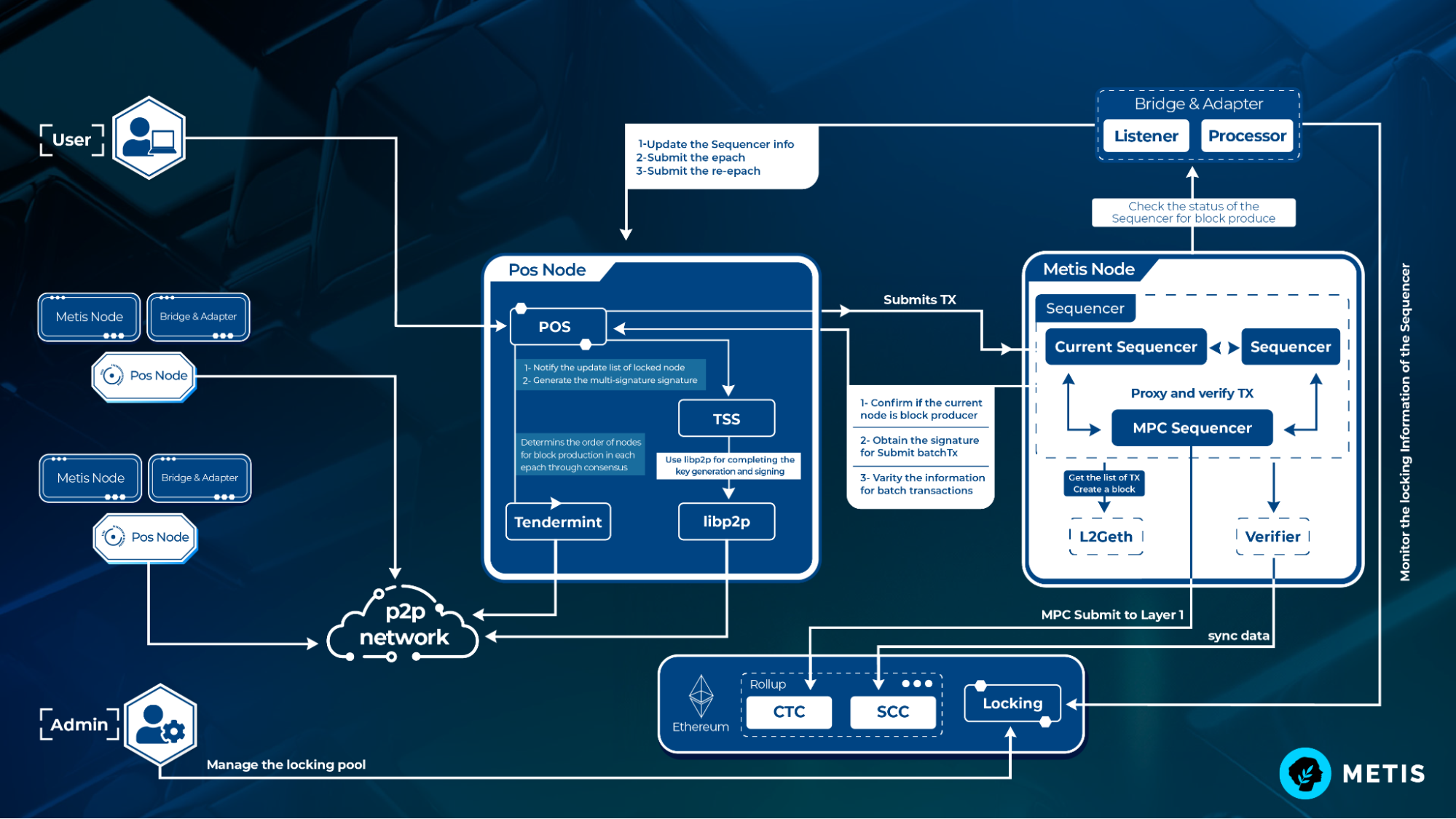
Within their pursuit of scalability and price-effectiveness, many layer-2 systems adopt a centralized method of on-chain transaction processing, presenting just one reason for failure vulnerability. The Metis blockchain, however, has pioneered a distributed sequencer pool to enhance security and decentralization.
The Ethereum blockchain introduced smart contracts to automate certain occasions around the network, lounging the building blocks of decentralized finance (DeFi). Because the DeFi ecosystem continues its exponential growth, however, the constraints of Ethereum have grown to be obvious.
Despite last year’s migration to proof-of-stake, partly addressing the scalability problems with the Ethereum blockchain, the Ethereum network remains costly with regards to gas charges — the price of each transaction performed around the blockchain. On the top of this, the large decentralized world built on Ethereum makes network congestion around the first layer a normal occurrence.
Because of the decentralized and open-source nature from the Ethereum blockchain, developers have built numerous systems on the top from the first layer — known as “layer-2 blockchains” — to repair specific limitations. Right after, layer-2 (L2) systems that provide faster transaction speed or lower gas charges, including Arbitrum and Optimism, emerged.
Sequencer — answer to order on blockchain
However, one common aspect present in most layer-2 projects is they depend on one sequencer, which results in a vulnerability associated with centralization. But what is a sequencer?
In blockchain terms, a sequencer operates just like a traffic controller for on-chain transactions. A blockchain sequencer first collects on-chain transactions that might be incorporated inside a specific block. It puts transactions so as — an important step for that network to operate normally. The sequencer then places individuals transactions inside a block, making certain the block is filled properly as well as in the best order.
Relying on one sequencer for ordering and placing on-chain transactions introduces a vital vulnerability referred to as a anchorman of failure (SPOF). If the sequencer malfunctions as a result of cyberattack, technical glitch, or outdoors intervention, the whole blockchain network involves a dead stop. Furthermore, just one sequencer may struggle to handle growing transaction volume, resulting in scalability issues. To deal with these concerns, alternative solutions could be explored.
Decentralizing the network controller
Metis, a layer-2 Ethereum scaling solution, features a decentralized sequencer pool to improve the transaction speed and throughput of blockchain while keeping Ethereum’s decentralization and security. Going past the single-sequencer model utilized by Arbitrum, Optimism, along with other L2 projects, Metis is moving out a distributed pool of sequencers — a brand new concept with built-in risk management that keeps the network up even when one of the numerous sequencers within the pool goes lower unconditionally.
The sequencer pool model works together with Metis’ existing decentralized peer-to-peer validators and block producer network to allow smooth and secure sequencer transitions while removing faulty or malicious nodes.
The architecture of Metis’ decentralized sequencer pool. Source: Metis
Using the decentralized approach, individual sequencer nodes could be produced by whitelisted users. Metis has additionally announced a staking mechanism to do business with the sequencer pool. Users will have to supply many locked METIS, the native token from the Metis network, to function a sequencer node within the pool. By incentivizing staking with yields, Metis aims to obtain more sequencers onboard and progressively reduce the circulating supply.
Community-driven network
Faithful to the decentralization ethos, Metis intends to utilize the strength of community to grow its network and keep its network highly accessible by having an easy-to-use Web3 building atmosphere. The woking platform provides a streamlined consumer experience with gas charges that cost “less than the usual penny” while supplying among the fastest transaction speeds present in any L2 solution.
To promote community engagement and encourage participation within the approaching launch of their decentralized sequencer, Metis is hosting its Community Testing event. The wedding allows testers to earn rewards and lead to the introduction of the work prior to the sequencer pool goes live.
“Metis is happy to unveil the very first-ever layer 2 sequencer pool,” stated Tom Ngo, project lead at Metis.
“We invite the whole blockchain and crypto communities to sign up in Community Testing. By joining, users are assisting the main blockchain mission of decentralization while accruing attractive possibilities for every tester.”
Because the blockchain ecosystem grows with new projects, maintaining your primary support beams of decentralization intact is vital. Using its innovative method of how blockchain operates, Metis’ decentralized sequencer pool addresses the SPOF vulnerability and keep its mission of rewarding the blockchain community in focus.
Disclaimer. Cointelegraph doesn’t endorse any content or product in this article. Basically we are designed for supplying you with all of information that people could obtain within this backed article, readers must do their very own research when considering actions associated with the organization and bear full responsibility for his or her decisions, nor can this short article be looked at as investment recommendations.