When Ethereum premiered in This summer 2015, the planet was brought to the idea of smart contracts that wished to transform the blockchain space and permitted anybody from developers to enthusiasts to deploy decentralized applications (DApps) around the Ethereum mainnet.
With assorted DApps presently in use across different blockchains like Ethereum, they provide many use cases including banking, gaming, finance, shopping online and social networking, by having an ever-expanding users list around the world.
Getting provided the infrastructure required for developers to produce innovative digital applications, Ethereum, however, has limitations for example limited scalability and gas charges, factors which are now inhibiting developers from building specialized solutions that may rival popular centralized platforms like Twitter, Facebook and Netflix.
To overcome these challenges and explore the options of blockchain technology, Ethereum co-founder and it is first chief technology officer Gavin Wood left the Ethereum Foundation and founded Parity Technologies to construct blockchain infrastructure that will help produce the first step toward a decentralized web, or Web3 as it is termed.
Related: Five major challenges within the blockchain industry
Equipped with an enormous industry experience and deep knowledge of creating blockchains, he went ahead to construct Substrate being an open-source and future-proof blockchain framework for developers to construct on, enabling these to tweak their blockchain’s architecture consistent with altering customer preferences.
Substrate-based blockchains could be integrated as parachains on systems for example Polkadot or Kusama and provide an advanced of interoperability, assisting to provide market truly decentralized real-world solutions which are faster, cheaper and safer than in the past.
What’s substrate blockchain and just how do you use it?
The vision of Web3 as being a decentralized blockchain-based form of the web depends upon developers having the ability to create different blockchain applications that may communicate with one another with systems for example Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Typically, a blockchain framework can be used by blockchain developers to produce such applications by using in-built templates, they are able to save lots of development time at the fee for limited personalization ability.
This is when Substrate, a wide open source blockchain framework for building customized blockchains, is enabling developers to rapidly build blockchains according to field-tested code that’s powering a sizable ecosystem of blockchain projects around the globe.
Comprising a voluminous assortment of tools and libraries, Substrate may be the primary blockchain software development package (SDK) which was accustomed to build the Polkadot layer- protocol and could be utilized by developers to produce any kind of blockchain.
Related: What’s the main difference between blockchain layers L0 and L1?
The main block associated with a blockchain may be the node and uses decentralized network of those nodes or computers that talk to one another to keep the present ledger using the latest transactions. Each node inside a blockchain network can serve as both client and also the server, requesting and answering demands for data according to needs.
Why is a Substrate node unique may be the means by which these operational responsibilities are divided horizontally to supply a modular framework for building blockchains. Each Substrate node utilizes two primary elements: an outer node that handles network activity along with a runtime that determines transaction validity and accounts for handling changes towards the blockchain’s condition transition function.
The outer node accounts for contacting other nodes, handling the transaction pool, peer discovery and answering remote procedure calls (RPC) or browser demands using Substrate’s RPC Application programming interface (API). By querying the Substrate runtime or by supplying it with information, the outer node uses specialized runtime APIs additional communication.
Using the Substrate runtime handling exactly what happens on-chain, it’s the core element of the node for building blockchains and controls how transactions are incorporated in blocks, how blocks are came back towards the outer node or the way the chain condition is altered as a result of transactions.
Using host functions to talk with the outer node, the Substrate runtime enables runtime validity checking and multi-platform compatibility, supplying validation proofs for relay chain consensus mechanisms and offering support for fork-less upgrades towards the node architecture.
So how exactly does Substrate allow you to produce a custom blockchain?
Substrate offers greater freedom, versatility and much more optimization abilities than building on the top of the general-purpose smart-contract blockchain like Ethereum. Furthermore, Substrate-based blockchains can exist as “solo chains” or integrate into Polkadot or Kusama to get parachains.
Developers might want to begin having a Substrate node template, the fundamental unit in creating a blockchain using Substrate and offers lots of pre-built functionality with default implementations for aspects for example account management, consensus, fortunate access and peer-to-peer (P2P) networking.
These Substrate node templates are maintained within the Substrate Developer Hub and developers may also access Substrate’s large, active and useful builder community that’s continuously adding towards the ecosystem.
For additional complex projects, though, developers want a greater amount of freedom to find out their blockchain’s logic which is where Substrate’s Framework for Runtime Aggregation of Modularized Entities (FRAME) is necessary.
FRAME is among the most effective tools supplied by Substrate and comprises numerous modules and support libraries to simplify runtime development. These modules can also be known as Substrate pallets and represent customizable business logic to be used cases for example staking, governance, consensus along with other important activities that developers might want to use in the runtime.
Furthermore, developers may use its system, support, and executive pallets to supply a huge selection of services for that runtime atmosphere. While it’s possible to develop a Substrate-based blockchain without needing FRAME, the various pallets and libraries enable developers to write a custom runtime logic by utilizing its predefined components like a beginning point.
By mixing pre-built and custom pallets to infinitely control the characteristics and functionality supplied by the Substrate blockchain, developers is capable of specific results having a high amount of versatility and convenience.
How you can make your first blockchain on substrate?
Regardless if you are a new developer or someone with prior experience of utilizing a blockchain framework, Substrate offers tutorials that concentrate on supplying hands-on experience and also the Substrate Playground for individuals who want to experiment with little guidance.
Substrate tutorials are appropriate for absolute beginners, covering all steps without going much in to the coding details. Aside from these tutorials, Substrate provides numerous how-to guides on specific topics and furthermore grants use of many free projects which have been built using Substrate.
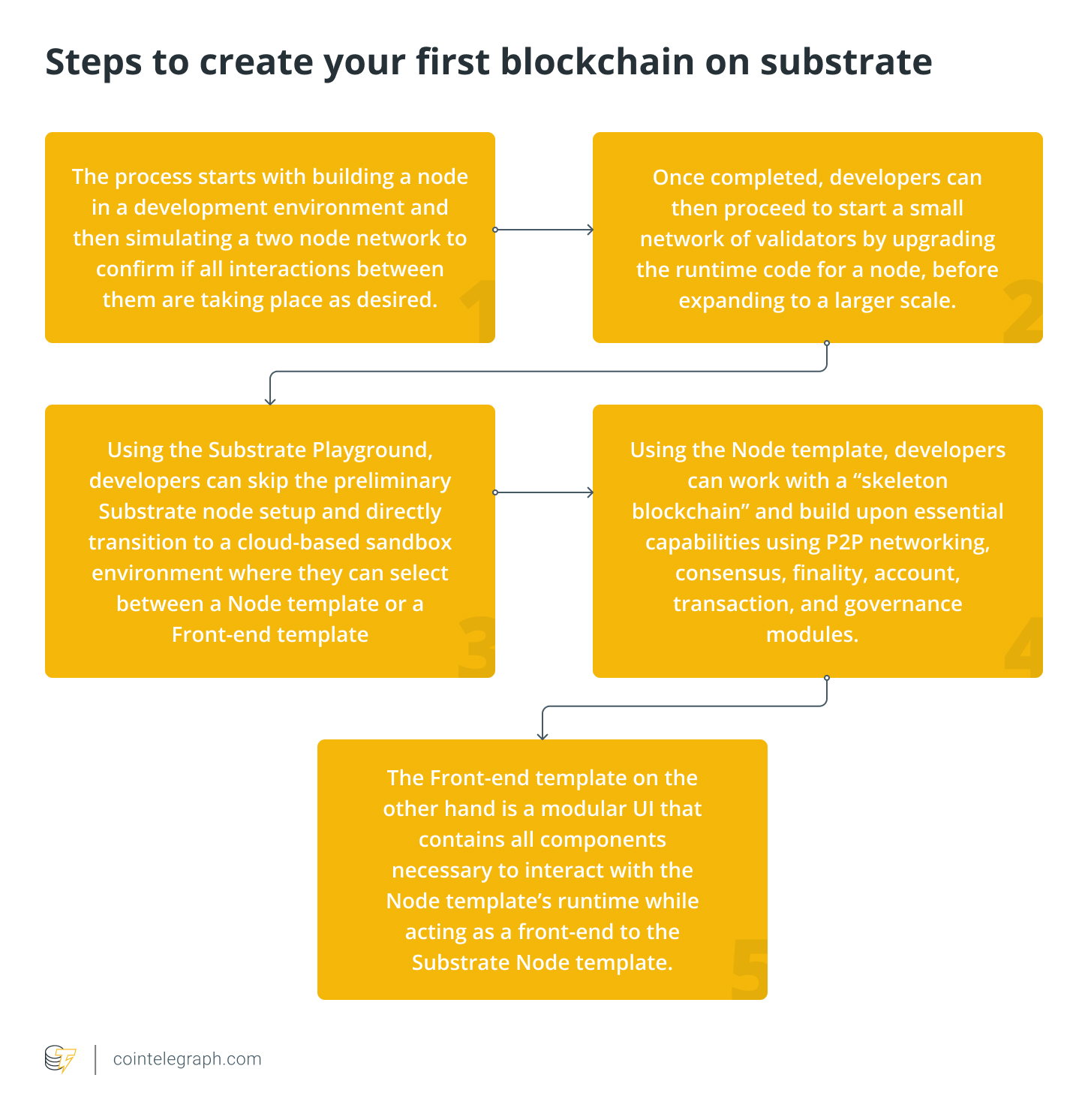
However, you should learn how to use pallets on Substrate to be able to personalize each node’s logic to ensure that you can use it along with smart contracts to include much more functionality within the resultant blockchain.
Thus, Substrate offers all necessary support from installation to effectively running your personal custom blockchain. Although it does not have a local crypto-token, the Polkadot (Us dot) token is most used thinking about the truth that it works with other parachains within the Substrate and Polkadot ecosystem, reflecting its concentrate on interoperability and scalability.